Megabot Madball Challenge
External Links
Aim
The aim of the competition is to build a robot which can locate tennis balls on a playing field and deposit them into bins.
My aims for this project were to increase my robot simulation abilities in the Gazebo simulator, and improve my skills in using the ROS tf2 transformation library by using it for robot localisation.
Hardware
The holonomic base (steppers and laser-cut acrylic) was built by my teammate, Shane Gingell. The base consumed x,y,yaw velocity commands and emitted the current pose of the robot based on wheel odometry.
I built the lifting mechanism, the basic operation of which is shown in the video below.
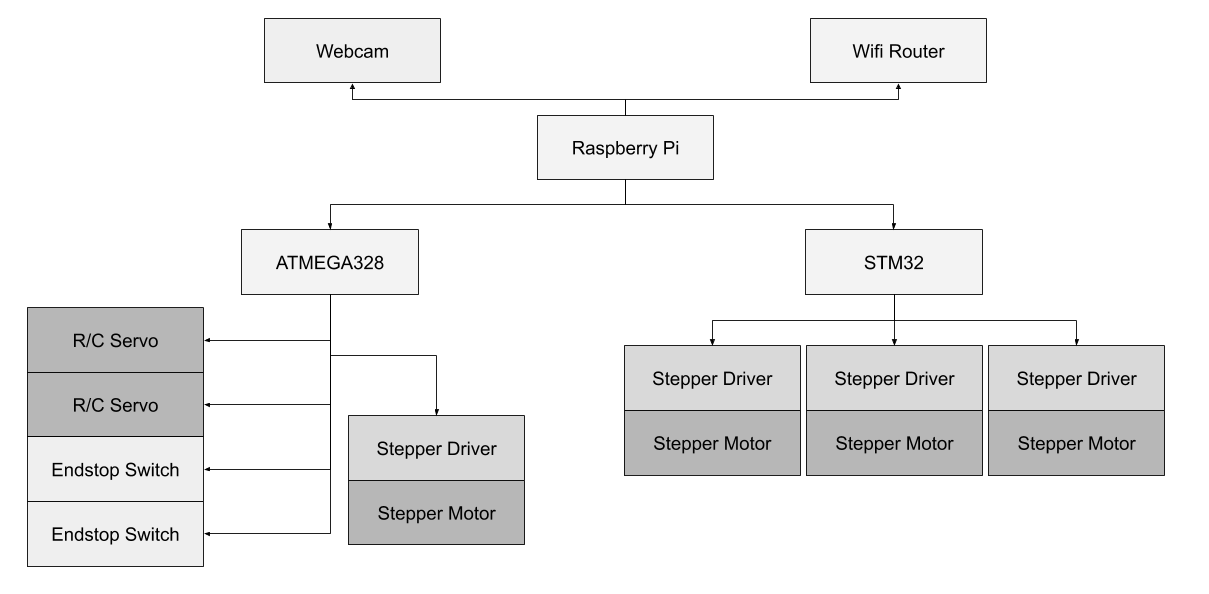
The robot uses a Raspberry Pi 4 for all high-level processing. Motor velocity control and wheel odometry is done using an STM32 microcontroller. Basic control of lifting sensors and actuators is done using an ATMEGA328 on an Arduino mini board. Both daughterboards are interfaced to the Raspberry Pi using rosserial, which uses UART as the transport. The following picture gives a general overview of the system setup.
Simulation
The robot was simulated using Gazebo simulator with ROS integration. The purpose of the simulator was to develop computer vision algorithms, code for localisation, and code for motion control, without the need for robot hardware. This was useful since the robot was not built unit about 2 months before the competition day.
Localisation
Localisation is done using computer vision an the ROS tf2 library. An image processing algorithm locates the tip of white lines located on the playing field. A correction transform can then be applied to adjust for odometry drift by knowing the measured and expected position of the line tip.
After this localisation, the balls can be located in the global map frame. The video below shows an example of ball localisation in the map frame.
Behavioural State Machine
Smach is use for behaviour sequencing. This is ROS-integrated state machine library with support for calling standard actions and services. Using this state machine library allows complex behaviours to be encoded in a simple to understand and easy to visualise manner. Smach also allows real-time viewing of the current robot state which imprvoes debugging ability.